There are a large variety of objects which can be seen in exquisite details with a modern microscope. While a microscope with under 1000x magnification will suffice in many cases, having a microscope with a high magnifying power such as 2500x is all the more power for exceedingly close view of minute structures at a scale appropriate for examination and analysis.
Disclosure: This post contain affiliate links, we may earn advertising commissions for sharing products we know and love.
Here we will take a look at some of the objects that can be seen under a 2500x microscope and the details at which they can be observed.
We will also look at some of the technical aspects of microscopy as it relates to photomicrography, the field of science where microscopes are used to digitally view objects and their characteristics that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
What can you see with a 2500x microscope?
Generally speaking, objects that can be viewed with 2500x can also be seen with less magnification, such as 400x—albeit in relatively less detail. See also, 7 Best microscopes for microbiology.
Here some objects with their interesting features will be discussed as viewed with 2500x magnification.
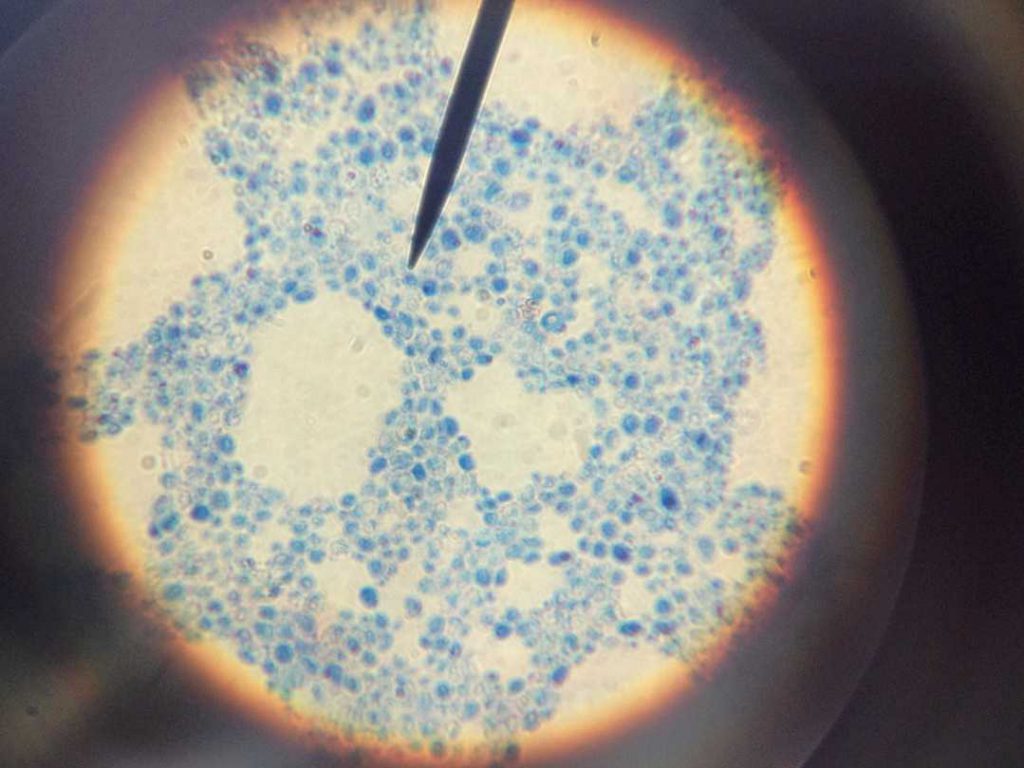
1. Bacteria cells
Close up view of light blue pen shine round zoom lens pointed at bacteria cells.
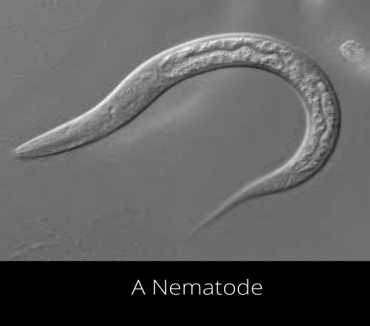
2. Nematodes
Nematodes can be observed under a 2500x microscope. The roundworms or nematodes are members of phylum Nematoda and there are plant parasitic nematodes being known as eelworms.
This diverse animal phylum inhabits a wide range of environments.
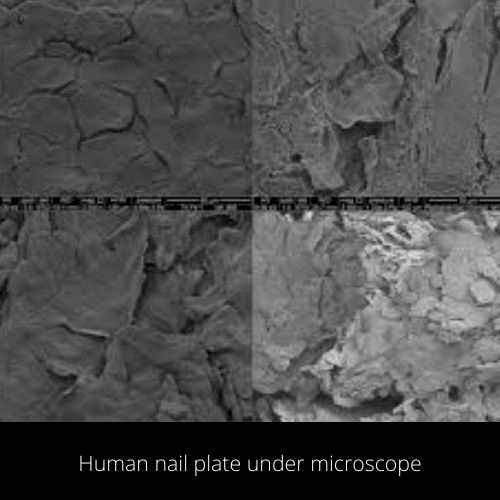
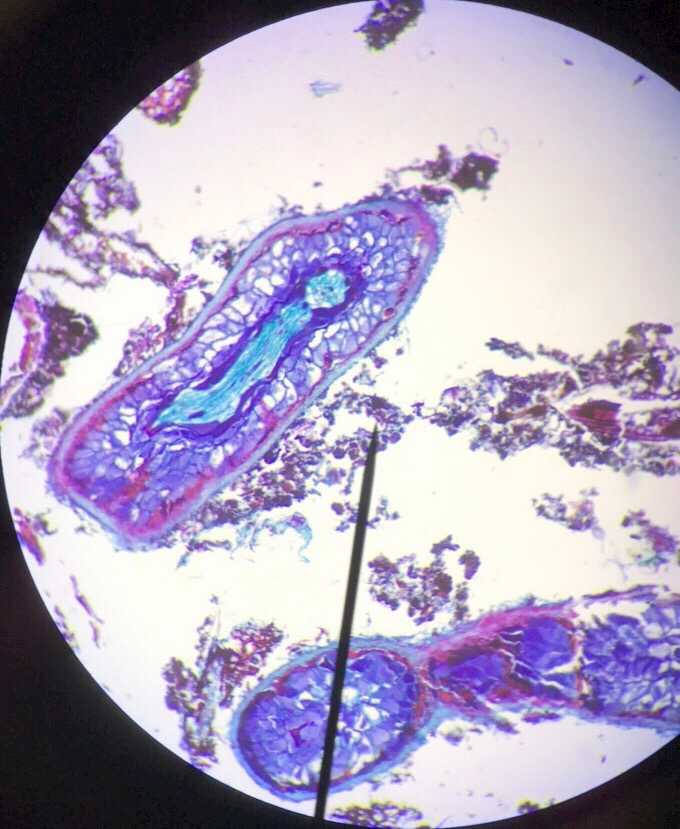
3. Nail fungus
Nail fungus is a very common infection characterized by yellow or white spots of the fingernail or toenail.
Nail fungus causes discoloration, thickness and crumbles at the edge of nails. Nails with fungi under the nail plate can be easily observed using 2500x magnification of compound microscope.

4. Fungi Cells
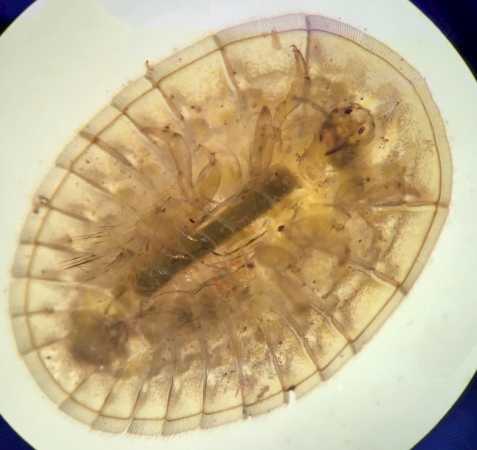
5. Water Beetle
Water penny beetle under a microscope
6. Old plantar warts
Plantar warts are miniature growths appearing most commonly on the heel or other areas of feet or hands. This disease is the result of a virus infection named human papillomavirus (HPV).
The mentioned virus enters the body through cuts in the skin. Immune system kills the virus but sometimes it grows and develops the warts. Plantar warts are contagious. In pictures you can see how warts appear under a microscope.
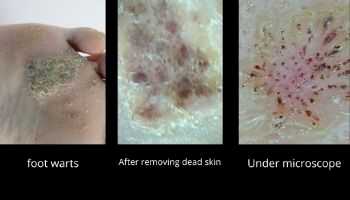
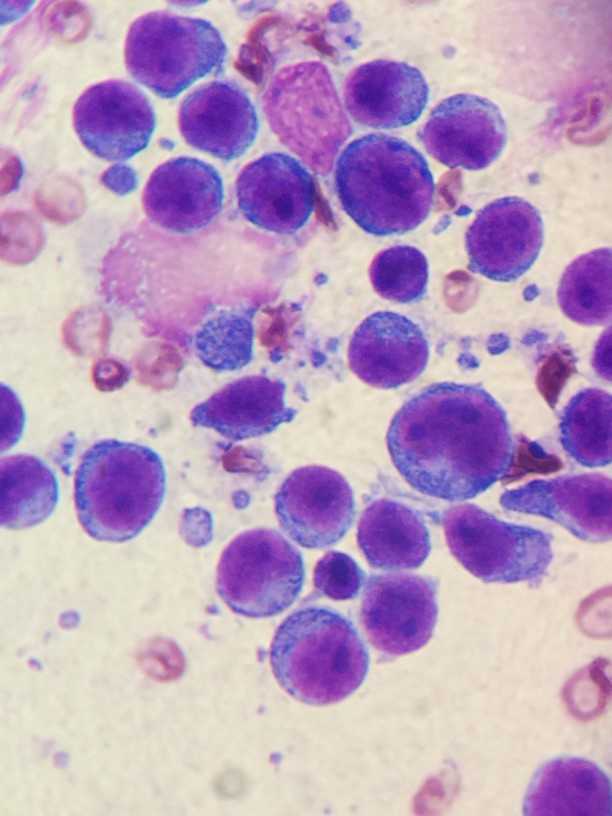
7. Cancer cell
K-9 lymphoma viewed through a Nikon microscope
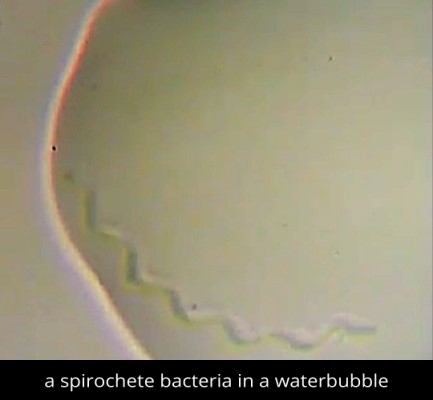
8. Spirochete Bacteria
The spiral shaped bacteria shown below are known as spirochete. They have a filament and diderm (double membrane). They’re a type of pathogenic bacteria.
In a sample of dirty water, you can observe a spirochete and its movement. Spirochetes move in a zigzag manner like a snake.
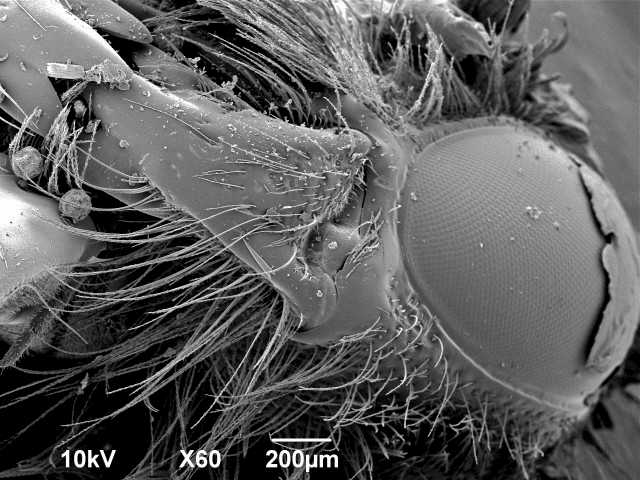
9. Bee’s head
Scanning electron micrograph of bee’s head with pollen

10. Bacterial movements
You can observe random and fast-moving bacteria without specifically differentiating them. The bacteria are first cultured and then are placed under a microscope.
The specimen of bacteria shows very fast movements of bacteria and bacteria move randomly. You can not exactly define the shape and type of bacteria here as their movement is fast.

11. Live footage of Amoeba
In a drop of water that you can take from outdoors, you can observe amoeboid movements. Amoeba moves in a circle around its own axis.
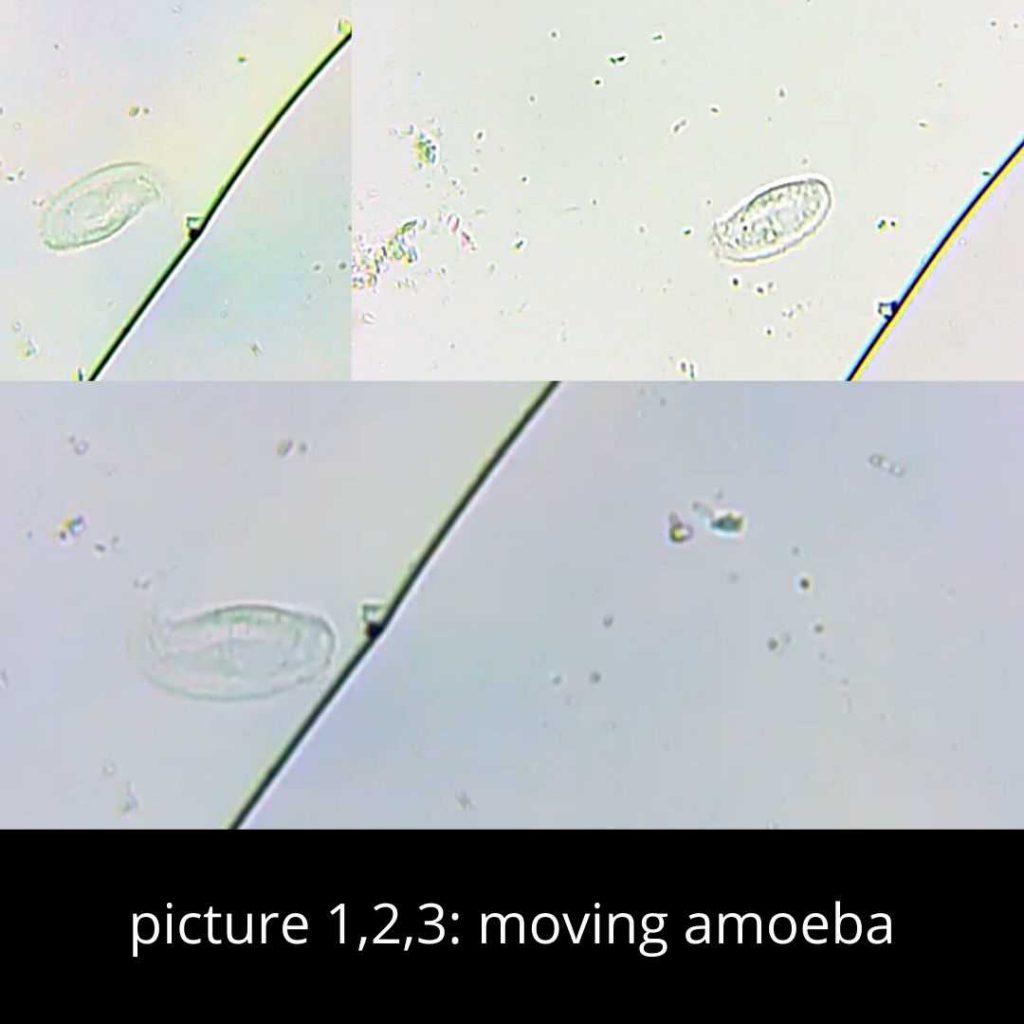

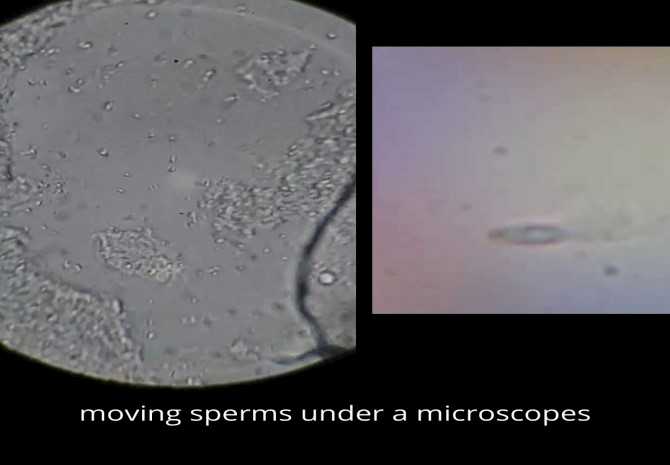
12. Observing sperm cells
An interesting part of 2500x microscopy is that you (as a male gender obviously) can observe your own sperms. You can check the motility and viability of sperm cells. You can count them as well. You can also confirm the situation of their morphology.
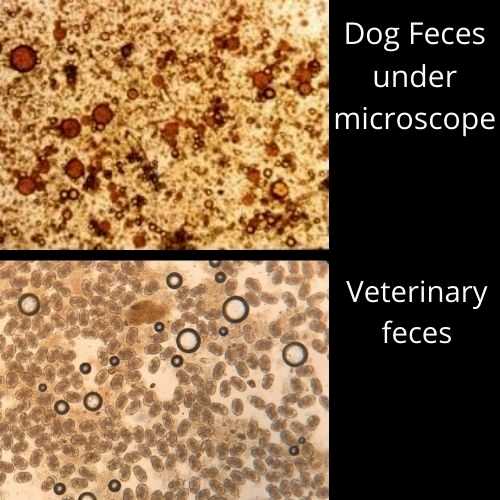
13. Fecal viewing
Urine or feces can be examined under a 2500x microscope in order to check for parasites, worms, or any other microorganisms that cause health damage to humans or animals. You can have your own stool analysis to perhaps check some conditions that affect the digestive tract. Note that these types of diagnostic analysis are best left up to the trained eyes of doctors and the like.
14. Mouth Swab Spirochete bacteria
Taken from a sample of mouth swab of a patient with progressive M. Alzheimers disease that shows spirochetes and a flagellated borrelia bacteria. You can even visualize very small spirochetes shorter than 3 micrometers and less than 1 micrometer in diameter.
They move so rapidly that normal video resolution at 25 frames per second fps cannot resolve their shape. If you set the frame rate at slow motion, all quickly moving flagellated bacteria can be seen much more clearly due to 100 fps high speed video recording.
In a microscope you can clearly see the shape of a 10nm thick bacterial flagella moving very fast. A yellowish spirochete can be observed eating another bacterial species.
- Koroknay, Zurich, Switzerland)
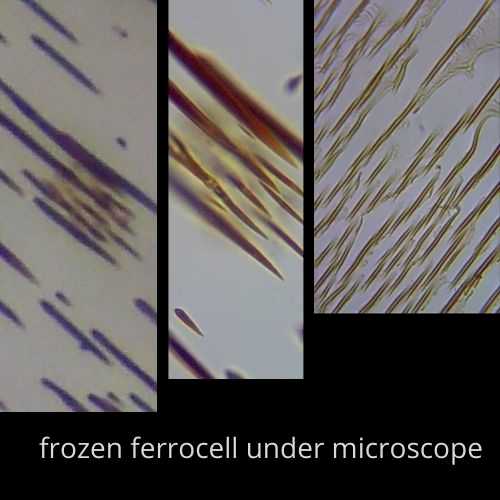
15. Frozen ferrocell or ferrostill
Ferrocell is a good magnetic field viewer. It’s easy to make but you should take precautions while dealing with ferrofluid. It is easy to take pictures of the ferrocell as they are not moving. They appear still and pointed at one end.

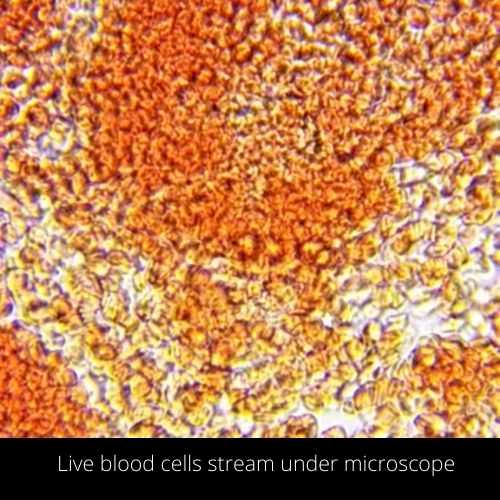
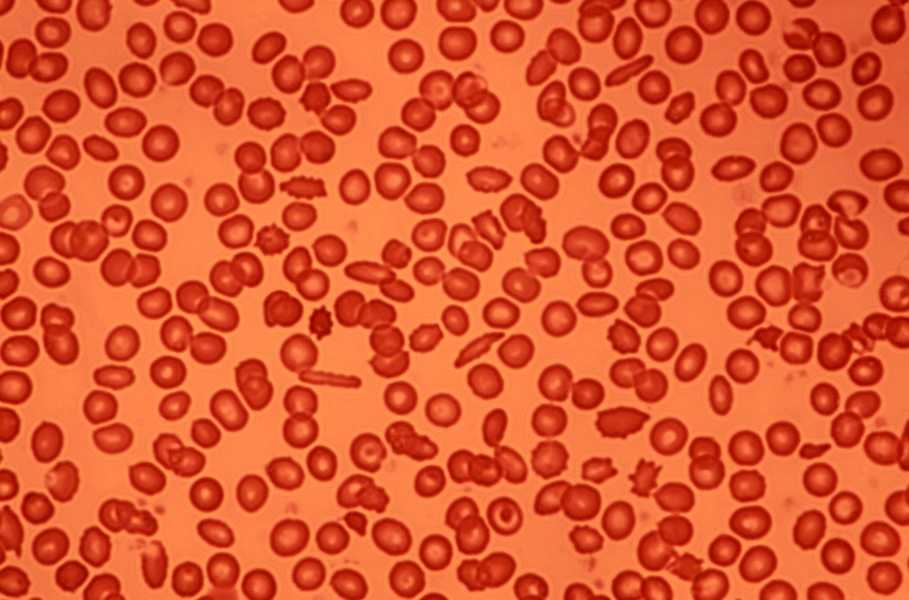
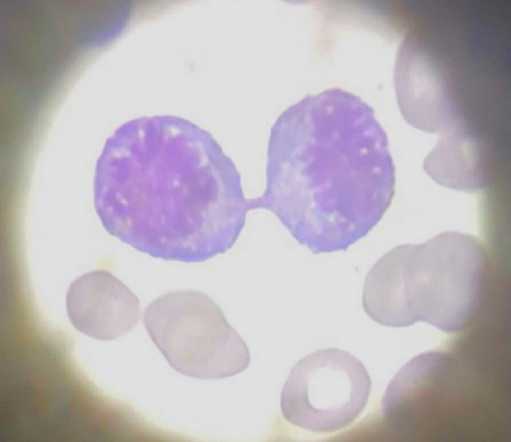
17. Live human blood
You can see the live video of human blood and movement of blood cells as a current in a stream.
18. Chapstick
You, for your amusement or interest in cosmetics, can observe different types of lip balm under a microscope. You can`t see the actual color of Chapstick. You will observe dark yellow or red colored spots in the sample.
19. Human hair
View of a piece of brunette hair

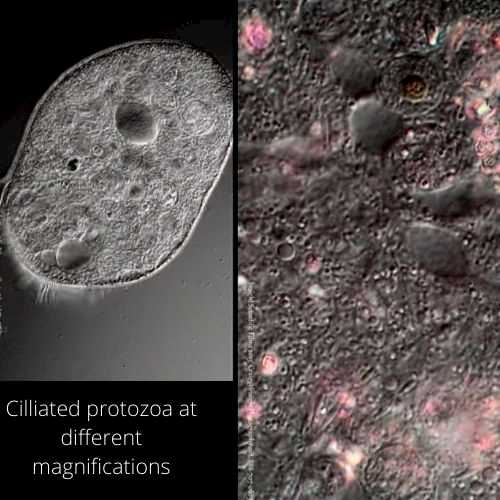
20. Ciliated Protozoa
Protozoa are single cell eukaryotes. A contractile vacuole contains water and is present in the body of protozoa. It increases in volume, and finally discharges its contents to the outside. You can observe the formation and release of contractile vacuoles. You will also observe the fast movement of cilia.
21. Yogurt
Observing diluted yogurt under a microscope is an interesting thing. Stain the bacteria with gram stain and observe them at 2500x. Your eyes will catch rapid movements of bacteria. You will also observe beneficial bacteria called probiotics that aid us in digesting.
22. Dentin morphology of root canal surface
Denton is calcified tissue and forms the major part of the tooth. Dentin morphology is basically observed under scanning electron microscope at 2300x, 2500x and other magnifications.
You can analyze that the root canal dentin is going from coronal to apical zone and hence you can find the ratio between the intertubular dentin area and the surface occupied by dentin tubules.
You see that dentinal tubules have a great diameter (4.32 micrometer) than the middle zone (3.74 micrometers) and apical zone (1.37 micrometer)
(journal of BioMed Research International, Article ID 164065)
23. Microbial colonization on leaves of Posidonia Oceania
This observation is done under electron microscope at 2500x and higher magnifications. Leaves of shoot of the seagrass Posidonia Oceania were observed. It`s observed that macro epiphytic growth was greater on outer leaf sides.
Microbial colonization density was higher on inner leaf sides, both on leaf surface and epiphyte surface.
Diatoms reach highest density on leaf tips and mature leaves. The bacteria have great number count on the oldest leaf and the leaf base.
Rod shaped bacteria were dominant at the basal part of young leaves. Small coccoid bacteria are dominant at distal and old leaf parts.
(Marine Ecology 5 (2), 143-190,1984, journal of Applied Sciences)
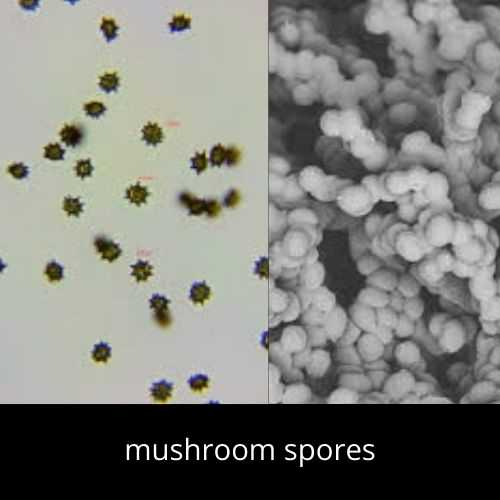
24. Mushroom spores
Spores are a source of identification of mushrooms. You can easily observe mushroom spores under a microscope. Spores` shape, color, size, attachment, and reaction to chemicals vary.

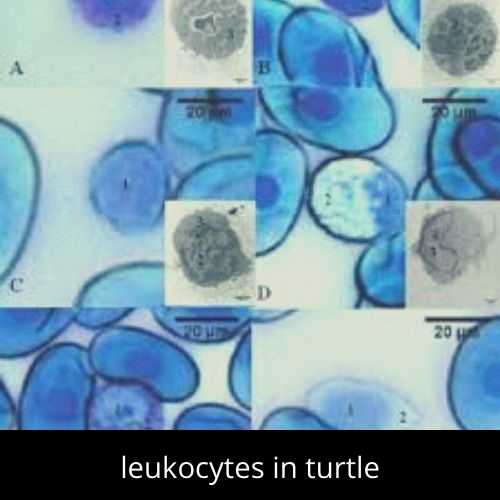
25. Leukocytes
Leukocytes are a part of the body`s immune system and help to fight infections and diseases. In mammals, leukocytes are easily identified due to protein stored in their cytoplasm and enzymes. You can observe the leukocytes in circulating blood of the turtle named Phrynops hilarri. The observation is done at 400x, 2500x and 2800x.
(Int. J. Morphol.,25 (4) : 677-682, 2007.)
26. Latex particles
Mono layer of synthetic particles is observed under a 2500x microscope.
(Volume 33, No. 2, April/May/June 2007, ISSN 0826 6220)
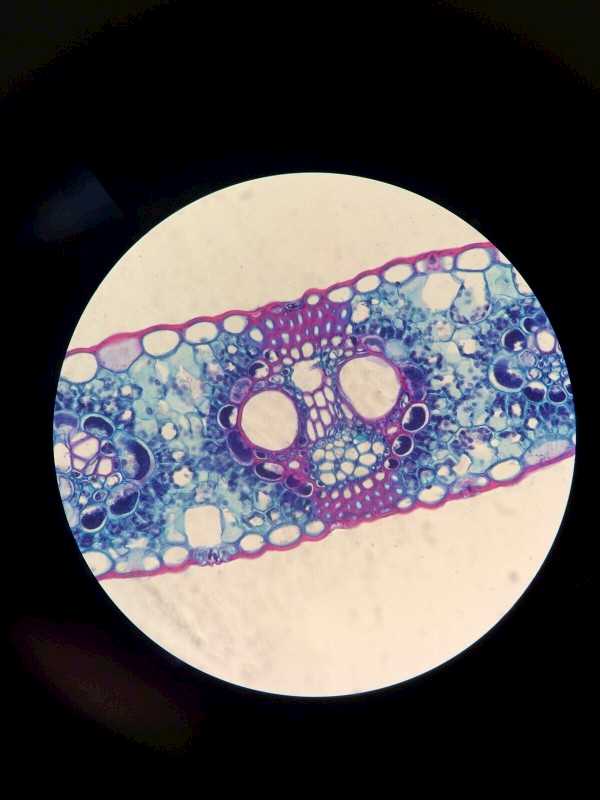
27. Monocot leaf
28. Microbes in untreated water
Using a scanning electron microscope at 2500x magnification power, bacteria, algae, sea urchin, amoeba and protozoa can be observed.
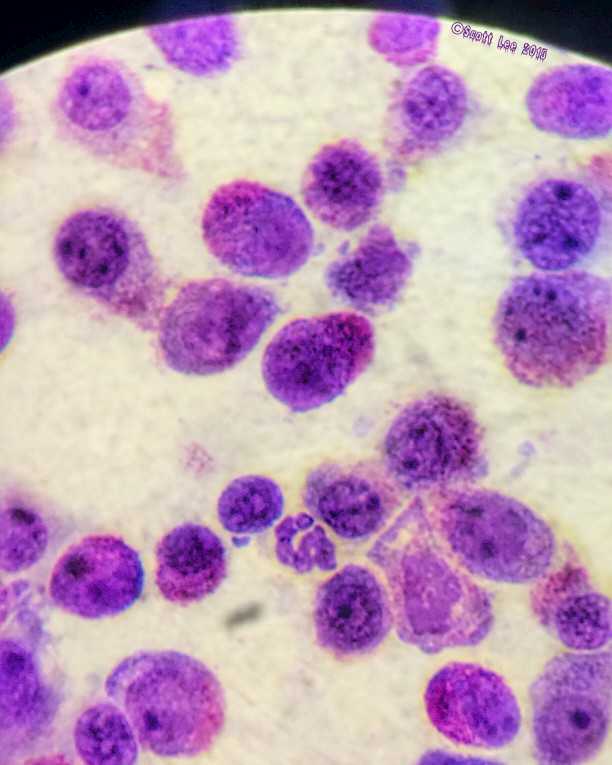
29. Mast cells
Mast cells shot through a Nikon microscope
30. Bacterial Attachment on Grooved Abutment
Healing abutments are placed on dental implants. The coronal portion of abutment is vulnerable to bacterial colonization.
We study the attachment of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum on titanium alloy abutments used for healing. In this one was grooved and other was smooth.
Bacterial growth observations are done at 25000x
- You can observe Fusobacterium nucleatum attached as on the border line between smooth and grooved parts.
- You will see a high number of Fusobacterium nucleatum within grooved parts of healing cap.
- Notice the low count of Porphyromonas gingivalis bacteria on the mechanical surface
- The growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis on the inner surface is high.
(Moses et al; In Vitro Preliminary Evaluation of Bacterial attachment , journal of Applied Sciences)
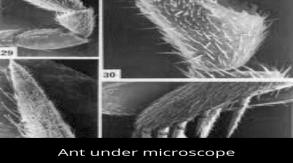
31. Ant specimen
Ant can be observed at 40x, 100x, 1000x and 2500x to have a look at its characteristics.
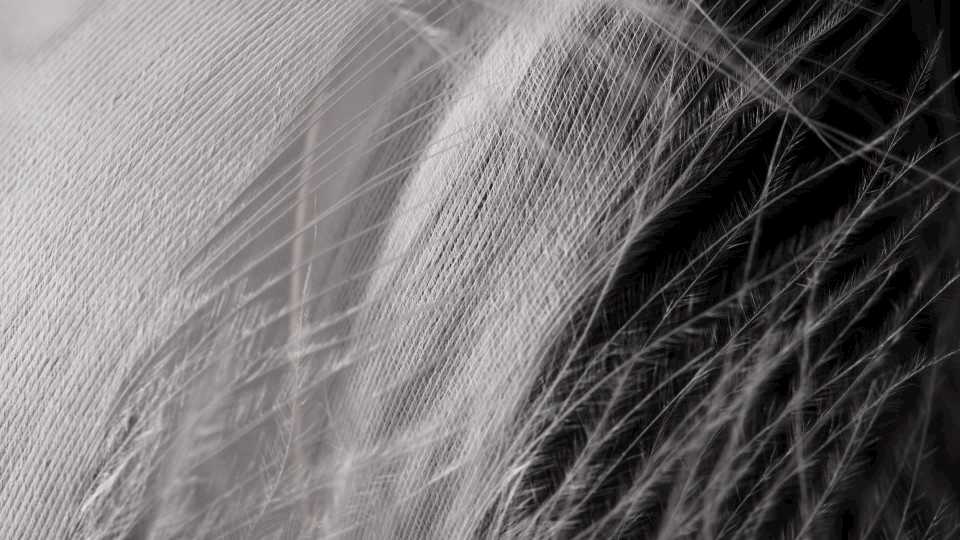
Bonus: Microstructure of feather
Beautiful rotating natural pattern of white feather bird

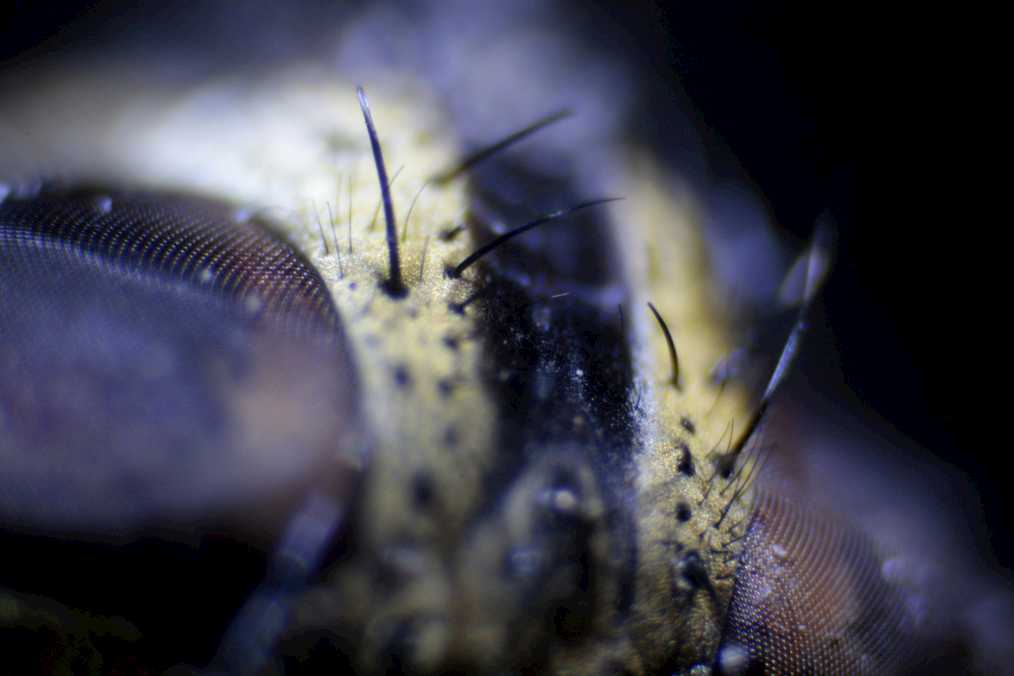
Bonus: Fly seen through a microscope

How microscopes see small objects
The magnifying power of a microscope is a dimensionless ratio and it defines that how many folds an object can be seen. It is usually expressed in the form 2500× (for an image magnified 2500 folds)
The resolution enables the view and measure of smaller details of an object. Resolution is expressed in linear units i.e. mostly micrometers (μm).
There are three well-known branches of microscopy: electron, optical, and X-ray microscopy, along with the scanning probe microscopy.
The optical, or light microscope uses glass lenses to form the image. Compound microscope creates the image relayed by two lens arrays, eye piece and objective. The objective has a short focal length and is used to form a real image in the front focal plane of the second lens i.e. eyepiece or ocular.
Other microscopes use the wave natureof varying physical processes e.g. electron microscopes.
The eyepiece forms a large virtual image that can be easily viewed and observed by the observer. A compound microscope has three further types depending upon the number of eyepieces and kind of view tubes: monocular, Binocular, and trinocular.
Image processing of a 2500x microscope
Photomicrography is the technique through which images of interest can be captured by photography using a microscope.
There are times when the image captured from a high-powered microscope is overblown to such degree that it requires additional processing and analysis to get a good perspective on the data. In this process some actions are performed on images in order to get an enhanced image and extract some useful information from it.
It is a type of signal processing i.e. input is image and output can be image or characteristics associated with that image.
Varying microscope technology see differently, therefore the specimen type and size may affect visibility depending on the type of microscope regardless of the magnification.
The basic actions for digital image processing systems are four
- accession
- storage
- processing
- display
Image processing being an integral part of research, is highly important to the fields of research and medicine. Now a day’s, designers design microscopes that allow them to connect to an image processing system.
Historically, until the early 1990s, most image acquisition in video microscopy was done with an analog video camera, often simply closed-circuit TV cameras. Today, acquisition is mainly done using CCD cameras mounted in the optical path of the microscope. The camera can be monochrome or full color. Today`s CCD detectors permit the high image resolution for image processing.
A common approach in image processing is to create an image mask which only includes pixels that match certain criteria, then perform simpler scanning operations on the resulting mask. It is also possible to make a video sequence of objects and label them.
Digital image processing program for microscopy
MATLAB is a software and a general-purpose programming language. MATLAB is used to process images and one generally writes script files or function files to perform the actions. These files are the record of the processing and are used to ensures that the final results can be tested by others.
Before selecting a software, you should analyze it on following basis:
- Do you have the required hardware (e.g. enough memory, suitable video board) to use the imaging software?
- Will this software be able to import files from all of the microscopes that you use?
- Does the software include all of the features that you need?
- Will you need to use more than one program to analyze your images? If so, can image and data files created by each program be read by the other programs?
- For commercial packages, how many additional modules will you have to purchase to meet your analysis needs?
Popular 2500x Microscopes
- 40X-2500X Binocular Laboratory Compound Microscope
- 40X-2500X LED Trinocular Biological Compound Microscope
- AmScope T690C-PL-10M 40X-2500X Achromatic Microscope
- Swift SW380T 40x-2500x Magnification, Siedentopf Head, Research-Grade Trinocular Compound Lab Microscope with wide-field 1
- OMAX 40x-2500x LED Digital Trinocular Lab Compound Microscope with 5MP Camera and Mechanical Stage





